The economy in India underwent the greatest tax reformation with the introduction of GST (or Goods and Services Tax), which is more or less a destination-based tax reporting structure. According to the latest policies introduced in India’s economic landscape, small businesses can now increase their realms by capitalizing on the prospects of GST. The GST filing process for small businesses is also considerably important similar to large businesses.
Gone are those days when small businesses and medium businesses were compelled to file multiple taxations; today, with the implementation of the composition scheme, the burden that was so long hovering over the businessmen’s minds have now been eliminated.
This implies that filing for a GSTR is inevitably compulsory, and every small business, medium, and large business irrespective of its size and sales must submit its report in due time (if no sales or purchases were made on your small business, medium, and large business, there will be a NIL report).
What is a GST Return?
A GST Return is a document that includes all the details of sales/income and/or purchase/expense, where a taxpayer must file with the administrative authorities of tax. These are used by the respective tax authorities to calculate the net tax liability.
A registered dealer under GST has to file the GST Return. The GST return filing should include,
- Sale
- Purchases
- Input tax credit (GST that is paid on purchases)
- Output Tax (GST paid on sales)
Who needs to file a GST Return?
All types of GST business dealers and business owners who registered under the GST system should compulsorily file this GST return. The GST Return has to be filed based on their perspective business or transaction.
How to Register GST for Small Business?
Registration of GST for small businesses is an easy process. GST registration for small businesses can be applied easily with the help of the GST portal. There are several firms offering online registration for your small business with GST.
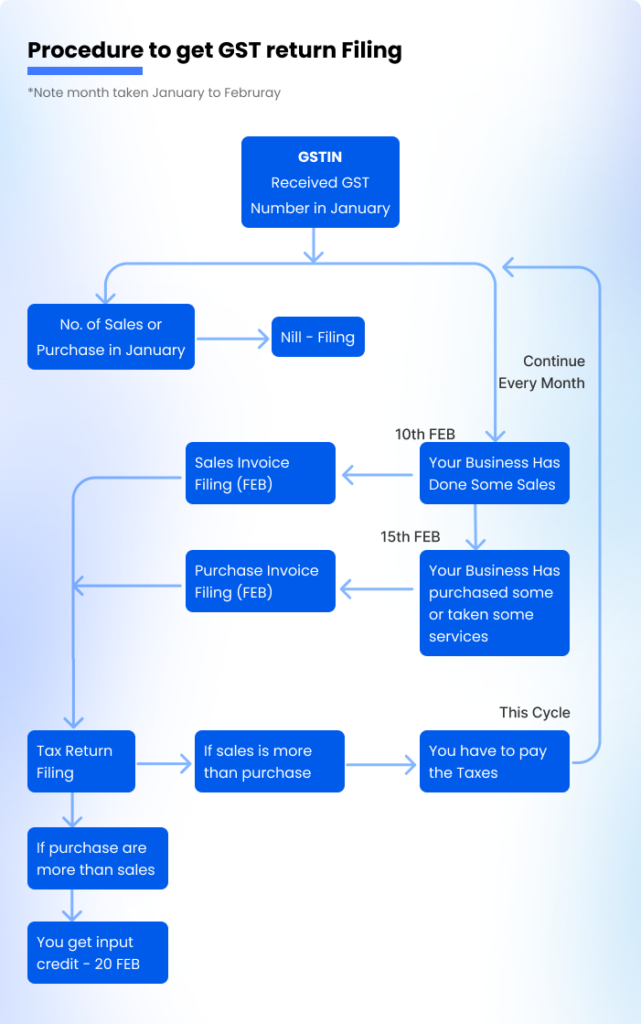
Process for GST return filing services online

GST return filing procedure
The Different Examples of Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
Generally, large businesses often have enough resources at their disposal to manage tax-related matters, whereas small businesses lack enough capital to maintain adequate accounting information and tax liability. The income tax department has introduced a more straightforward method for this large portion of small industries known as the Presumptive method, where the income is calculated as per gross receipts of the business.
Usually, most small businesses have an annual turnover of 50 lakhs or less; and with a configuration fluctuating within this window, paying the tax liability through a composition scheme becomes incredibly easy. However, even though all the previously variable taxes have now been combined into one, small businesses are lagging in funds and technological expertise that qualifies as indispensables in this procedure.
Ideally, simplification of the process requires every small business and large businesses to depend on GST software that would automatically calculate and generate invoices and at the same time, keep an accurate tab of the tax.
Tax Return Filing Obligations
Regular taxpayers file their GST returns after each month; but, for those under the composition scheme, filing GST returns quarterly, is compulsory. Small business and medium-sized business owners with less than 2 cr turnover every year have chosen the presumptive income tax scheme depicted under section 44AD, section 44ADA, and section 44AE. These labels are required to file their tax returns via the ITR-4 form.
But, that small businesses and other business owners who have avoided the presumptive income scheme and yet have profits that exceed 2 crores in 12 months’ time will have to file through the ITR-3 form. In the following segment, we will be mentioning the obligations of taxpayers who file under GSTR-4, GSTR-4A, and GSTR-9A schemes.
Small business dealers must have their expense history, split between GST registered and non-registered entities. The entire turnover or gross receipt as per GST and GSTIN must be logged while filing ITR-4. The details of both CGST and SGST/IGST paid on purchases, sales, and expenses must be specified under the profit and loss accounts, by small business owners who are filing their returns under ITR-3, ITR-5, and ITR-6.
You must also know that if any amount of input tax credit remains unclaimed as of the 31st of the year, must be mentioned under “Schedule OI” (Other Information) of the parallel ITI form. In all, all regular businesses alike should file two monthly returns and a single return.
But, the composition dealers will be needed to fill out returns separately. A composition dealer who attracts a turnover of more than 1 crore annually should pay the tax on total sales and that too at a specific rate. An interesting reminder here is that the dealer pays taxes under reverse charge purchases from the unregistered sellers and import of goods/services. But these dealers have the privilege of absorbing benefits from compliance and returns that are not upto the mark with tax payment at inexpensive rates.
GSTR-4
The GSTR-4 can be equated with GSTR-1, as both of the schemes have the same string of requisites and implications. Because small businesses are not eligible for the input tax credit, they are spared from filing the GSTR-1 and GSTR-2. In the GSTR-4, the taxpayer is expected to declare a precis of his outward supplies with accompanying details such as tax payable and tax payment. The return is to be filed on the 18th of every quarter-end, stepping beyond which will opens doors to a lump sum as the penalty fee and inability to file in the next quarter.
There is a total of 13 sections on the GSTR-4 form. After logging in to the portal, your name, GSTIN, and aggregate turnover will be automatically published on the page. Nevertheless, sections of information including outward supply, taxable inward supply, debit notes, imported goods and services, and credit notes can be corrected, if there appears to be a mistake. But, once all the details are confirmed, and the form is signed and submitted, there is no going back until the next quarter.
GSTR-4A
All seven parts of this form are auto-drafted by the GST system. It contains the credentials of the taxpayers, details of the debit and credit notes received, inward supplies received from a registered taxable person, and the modifications necessary from the earlier tax periods. Apart from the rudiments, the TDS credit received must also be updated on the form.
GSTR-9A
GSTR-9A concerns the annual returns for the compounding taxpayers. The other regular taxpayers must file under the GSTR-9A form. These annual return calls are to be filed on the 31st of December every year and the repercussion of refusing to file it attracts Rs. 200 each day. There are 5 parts to this form, namely:
- Details of the taxpayer
- Summary of quarterly returns registered in GSTR-4 for outward and inward supplies across the year.
- Crucial particulars of the tax paid in the financial year including late or penalty fees.
- Inputs about the modifications made in the preceding financial year.
- Details of the refunds, credit reversed, demands, and other penalties, if any.
These forms and their regulations apply for small businesses with a taxable turnover of fewer than 50 lakhs; nonetheless, if this bar is crossed, small businesses need to fill the GSTR-1,2,3B monthly and GSTR-9 annually.
Benefits of GST for Small Businesses
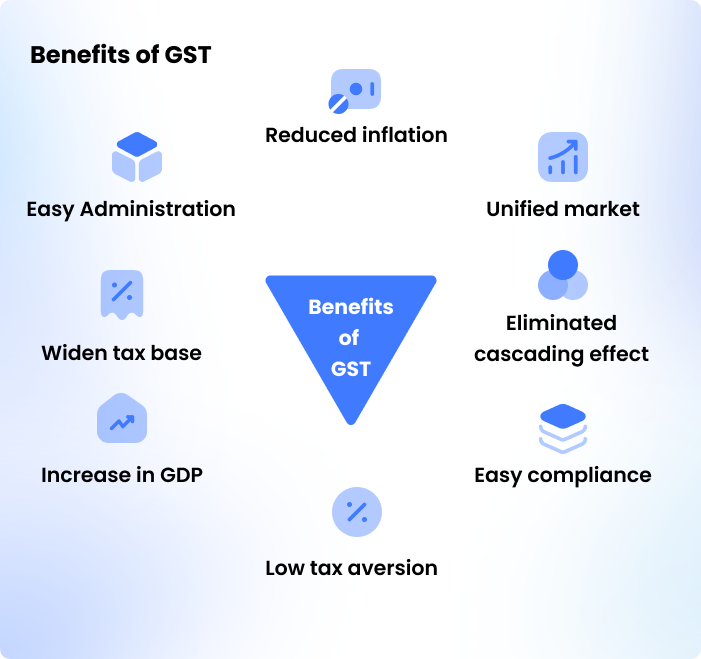
The GST for small businesses has benefited from the large impact. Depending on the small business profession, GST has its advantage. If you are a start-up business or a small business, then the following are their advantages.
- Under the GST Regime, small businesses or start-ups can pay their service tax and VAT as combined.
- The taxation process has made it simple and time-consuming. The GST for small businesses reduces the tax compliance burden.
- Starting your small business becomes easier by reducing high procedural fees.
- Cascading taxes are avoided, by dividing all indirect taxes into central taxes and state taxes. This helps small businesses more indirect savings.
FAQ's
What is GST Return?
A GST return is a statement of financial action by a respective taxable individual for a specified time period. It permits a taxable individual to self-assess the tax that they owe for a respective time period.
Is GST necessary for small businesses?
If you are planning to start a new business, businessers need to know about GST registration. Under the GST Act, every small businessers must register GST. It is important for every small businessers to get GST if you have a business annual turnover greater than 40 lakhs.
Can I charge GST if I’m not registered?
No, you cannot charge GST, if you have not registered your business for GST.
How to file GST for small businesses?
If you are looking to file GST for your small business, then make sure to check the article without skipping it. This will help businesses to file GST in the right way.
What is the purpose of filing a GST return?
Finalization of the tax liabilities of the respective taxpayer within the prescribed time period; to state tax liability for a provided period. Offering essential inputs for handling policy decisions. Compliance validation program of tax administration. Mode for transfer of data to the tax authority. Managing audit and anti-evasion schedules of the tax regime.
Who needs to file a GSTR?
Each and every registered taxable individual betrays the threshold boundary for payment of taxes.