In business, some customers receive faulty, broken, low-quality goods or else other unsuitable goods, the customer can return the product to the seller. In addition, the customer may also hold the product with them at a reduced price.
Thus, there exist two possibilities! If the customer tends to return the goods that are purchased, this type of situation is called sales return. And, if the customer accepts the damaged goods and requests for a cost reduction, it is called a sales allowance. induced
Every company tends to maintain both their sales return and their allowances account record in a single account.
What is a sales return journal entry?
In terms of payroll journey, the sales return is that which ought to be helpful for the returning customers in account books or to the account for when there exists a return of sold goods by your client because of unrequired goods/services by clients or may be due to problems with the sold goods, etc.,
Here is your journal entry to pass in account books for sales return accounting.
Performance and Classification of Sales Return
The sales return is reported and recorded in Sales Return and Allowances journal entry. Then the report is created on the income statement as a deduction from “Gross Sales”. Here follows the simple journal entry examples.
Journal entry – 1:
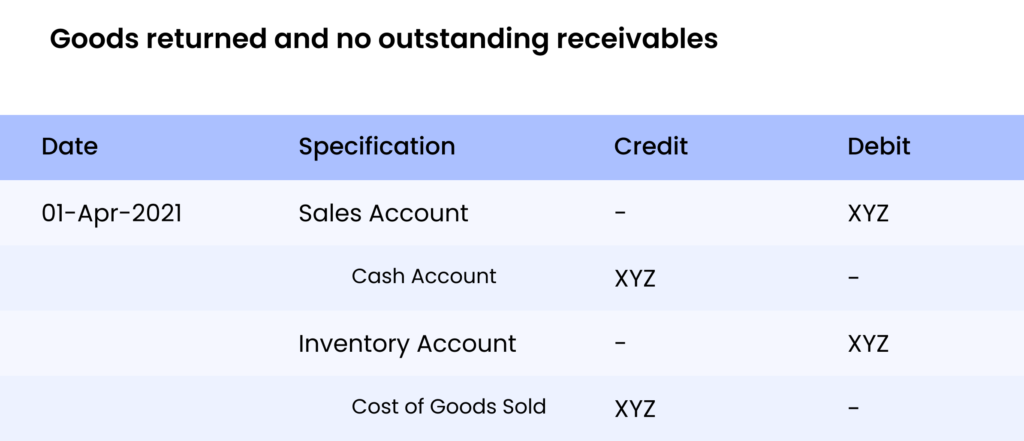
The above journal entry is limiting the sales by sales return.
Journal entry – 2:

The above journal entry is raising the inventory and tuning the COGS (Cost of Goods Sold)
Sales Return Journal Entry Examples
Here are two examples to get a clear view of the entry.
Example 1
George is running a retail shop. He sells his products. He mentioned in his invoice that if the customer buys the products and in case of any damage or other issue, then products can be returned within 30 days.
For June 2020, he made $6,00,000 sales (sales made on a cash basis is 40% and sales made on a credit basis is 60%). The outstanding receivables of George’s company are $3,00,000. He has $1,00,000 as cash on the balance sheet, at the end of August 2020. The COGS was $5,00,000. And the remaining balance on closing inventory is $4,00,000. 10% of Geroge’s sold goods, noted as return goods due to product damage. George’s gross margin on sales is 30%.
With the above-mentioned detailed report, George needs to pass the sales return journal entries. Additionally, the estimated remaining that remains on sales, cash, inventory, receivables, and the COGS (Cost of Goods Sold).
Solution for the above example information
First, calculate the amount of sales return. Here the sales return is 10% of $6,00,000 (thus, 10% of $6,00,000 is $60,000). Now, George passes the journal entry. He assumes the ratio of 40% return is based on cash and the balance of 60% return on receivables. As a result, a cash account credited by 40% of $60,000 is $24,000. Receivables account credited by 60% of $60,000 is $36,000.
Moreover, the inventories are limited by $60,000, which is less than 30% of the margin, which is $60,000 less than $18,000 i.e., $42,000 ($60,000 – $18,000), that will to added on inventory items and limits the COGS similarly.

Therefore,
Sales return journal entry

Adjustments to COGS

Example 2
Let us consider an XYZ private limited, which sells two products, bikes and cars, on an equal ratio of both cash and credit. George is an internal audit for the XYZ company. He draws two samples randomly to validate whether the company records its journal entry accurately. Note that the remaining balance must report on a fair and accurate basis.
- Sample No.1: Car
XYZ sold a car to Mr.James, which is $6,00,000. James purchased the bike on Feb 22nd. After some days because of some fault on the purchased car, James decided to return it to the company. James return the purchased bike on Oct 10th. His total amount returned to him on the same day.
The gross margin on the car is 30%
- Sample No.2: Bike
Mr. Robert purchased 3 bikes from the same XYZ company for $3,00,000. He decided to pay for one bike, and the balance payment was made outstanding. Robert purchased the bikes on Feb 22nd. After a few days, Robert noticed that there were some scratches on one of the newly purchased bikes. He decided to return the scratchy bike and handover it on Mar 1st. Since he has an exceptional amount, that was adjusted and balanced with the process.
The gross margin on the bike is 20%
With the above-mentioned details, you need to pass the sales return entries
Solution for the above example
Estimating the sales return value and the adjustment made on COGS.
- Sample No.1: Car
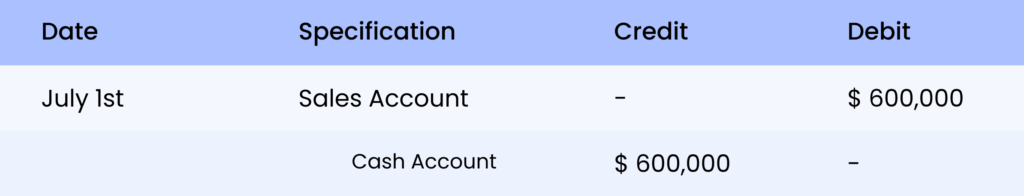
Sales for $6,00,000, adjusted for gross margin 30%. It is calculated as, $6,00,000 * 30/130 (thus, $138,462). The cost added to inventory is $6,00,000 – $138,461 which is $461,538

The Journal entry is,
- Sample No.2: Bike
Sales for one bike is 1,00,000 will be adjusted for a 20% gross margin. It is calculate as $1,00,000 * 20/120, i.e., $16,667. The amount added to inventory is $1,00,000 – $16,667, i.e, $83,333.

The Journal entry is,


Important considerations about Sales Return Journal Entry
There are more number organizations/companies, sell their respective products/goods either through credit basis or through the cash basis. The companies should check the ratio they maintain. Additionally, the entry information should be passed if any of the customer details are unknown.
There is an impact on revenue, which is, limited by debiting the sales account. Additional to revenue impact, there is a possibility to affect the company’s gross margin.
Since the COGS is further adjusted as sales return, it will result in increasing inventory. It is essential to look after the gross margin whether it is on sales or costs. Because if it is on cost, there is a need to adjust for weight. In the case of sales, you can limit the number of sales by that respective margin directly.
The reason behind adjusting the inventory and COGS for gross margin is sales return has not earned profits for the organization. Therefore, there should be a reverse in profit.
Journal Entry for Sales Return| FAQs
What is sales return in accounting?
A sales return is an inventory that is returned to the respective seller. The reason behind sending back the inventory to the seller might be due to any fault in the goods, shipping the wrong item, shipped and receiving late, or the received product specification might be wrong.
Regarding accounting, the merchant will record this respective return as the credit to the accounts receivable account and debit to the sales return account; The sum of the entire amount of sales returns in this respective account is considered to be the deduction from the reported cash of gross sales in a duration, which gains a net sales figure. The credit to the account of accounts receivable deducts the charge of accounts receivable due.
Are sales return an expense or revenue?
The sales returns have a direct impact on the net income, thereby deducting the income. It cannot be mentioned as an expense, but they contribute to the income loss.
How to Control Sales Returns?
Here are some of the tips to reduce goods return. These tips will help you control return goods and return goods journal entries.
- Start with quality control to decrease returns
- Represent product accurately
- Mention the exact and right size of the goods
- Try to get customer reviews and feedback
- Make sure to pack your item in the right way
- Mention the right delivery date
- Plan to follow the liberal return policy
What is the difference between sales return and purchase return journal entries?
- Sales return is nothing but the goods returned by a customer to the seller.
- Purchase return is operated for documenting the goods bought from the supplier which are returned to the supplier.
Related Article
Purchase return journal entry
The purchase returns (which are called refunds) and allowances are issued by the suppliers, on originally purchased products for resale. Read more