In the account payable process – the procurement and receiving stage, the 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way matching plays a vital role. It is worth investing in this control to make sure your business doesn’t pay for things you didn’t receive or overpay for things you did.
The topics we discuss
What is matching?
We perform the matching for goods and services ordered through your ordered purchase. Matching is a process that takes place during an online approval process. As applicable, the invoice matching is matched to 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way matching. That is,
- 2-way matching – Purchase orders
- 3-way matching – Receives information
- 4-way matching – Inspect information
The invoice should meet the required tolerance matching or the invoice is on hold, where you cannot make the payment until they resolve the hold. The hold can also be realized manually.
Key point: The 2-way matching is set to default for all the invoices. If you have the 3 way or 4-way matching requirement, then you must set that on every purchase order when created.
What are 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way matching? What’s their difference?
If you’re an accountant you may be familiar with the topic – 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way matching. Let’s dive deeper to know more about what is 2 way, 3 way, and 4-way matching and their difference.
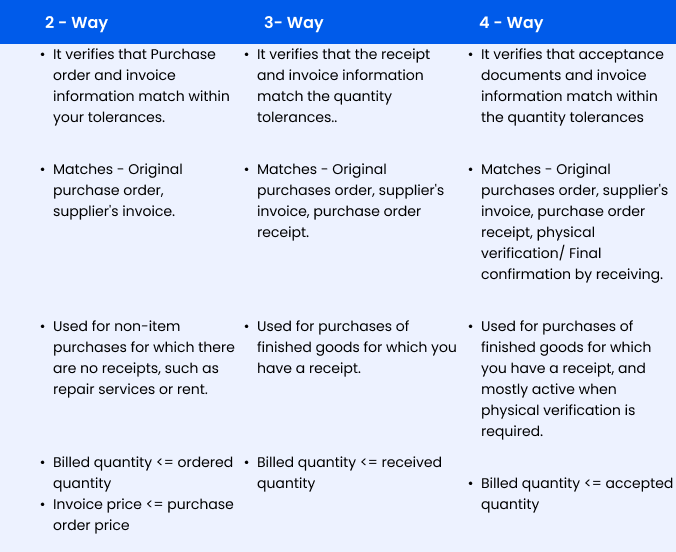
2-way matching
In 2 way matching, you have to verify both the purchase order and the information of your invoice match are with your level of tolerance as followed below,
- Does the billed quantity is less than or equals to your ordered quantity?
- Does the price of the invoice is less than or equal to the purchase order price?
3-way matching
In 3 way matching, the receipt quantity tolerances are compared to the invoice quantity tolerances. The 3-way matching defines,
- Does the billed quantity is less than or equal to your received quantity?
4-way matching
Additionally, the 4-way matching verifies the acceptance document and the invoice matches the tolerance quantity. In this 4 way matching, it verifies,
- Does the Billed quantity is less than or equal to the accepted quantity?
Tolerances
To determine your matching criteria, there is a requirement to set a tolerance. This is also critical. In some cases, most companies consider quantities inside the tolerance limits as matched.
Process of 2-way Matching
In the process of 2-way matching, we match the invoice’s quantity and amount to the corresponding purchase order’s quantity and amount. Here follows the 2-way matching process.
STEP 1: The vendor/supplier will send an invoice for the goods/services payment ordered via the purchase order.
STEP 2: To match the purchase order, an invoice is created on the accounts payable module.
STEP 3: Step 3 is an online approval process. In this step, match the amount and quantity of the invoice to the purchase order. Make sure whether they met tolerances.
STEP 4: Two states occur,
- Tolerance meet
- Tolerance not meet
If tolerance meets, place no holds on the invoice. Finally, the invoice approves for payment.
If tolerance does not meet, place a hold on the invoice, and proceed for step 5.
STEP 5: Either the reason behind the hold should be fixed or proceed for manual release of the hold.
STEP 6: Repeat the invoice approval process once you resolve the hold. If tolerances met, the invoice is authorized for payment.
Process of 3-way Matching
The process of 3-way matching arrives when an operating area uses an online receiving. In the 3-way matching process, you match the invoice with the respective quantity and amount of purchase order and the receiving information. Here follows the 3-way matching process.
STEP 1: Via the purchase order, the goods or services ordered. These ordered goods or services – will be received either to the appropriate operating zone division or the central receiving.
STEP 2: Perform a query on the purchase module by receiving the form to discover the relevant purchase order.
STEP 3: Enter the information and save all the information, including the quantity received into the Oracle receiving form (transaction screen).
STEP 4: Record the delivered goods on oracle. Then perform manually for receipt by the end-user.
STEP 5: On the accounts payable module, prepare an invoice. Match the invoice to the purchase order (Note that the purchase order is created on purchasing module)
STEP 6: Step 6 is an online approval process. In this step, match the amount and quantity of the invoice to the purchase order and the information received. Make sure whether they met tolerances.
STEP 7:
Two states occur,
- Tolerance meet
- Tolerance not meet
If tolerance meets, place no holds on the invoice. Finally, the invoice approves for payment.
If tolerance does not meet, place a hold on the invoice, and proceed for step 8.
STEP 8: Either the reason behind the hold should be fixed or proceed for manual release of the hold.
STEP 9: Repeat the invoice approval process once you resolve the hold. If tolerances met, the invoice is authorized for payment.
Process of 4-way Matching
The process of 4-way matching arrives when an operating area uses an inspection and online receiving. In the 4-way matching process, you match the invoice with the respective quantity and amount of purchase order, inspection information, and the receiving information.
STEP 1: Via the purchase order, the goods or services ordered. These ordered goods or services – will be received either to the appropriate operating zone division or the central receiving.
STEP 2: Perform a query on the purchase module by receiving the form to discover the relevant purchase order.
STEP 3: Enter the information and save all the information, including the quantity received into the Oracle receiving form (transaction screen).
STEP 4: Inspection information is recorded on the Oracle information form.
STEP 5: Record the delivered goods on oracle. Then perform manually for receipt by the end-user.
STEP 6: On the accounts payable module, prepare an invoice. Match the invoice to the purchase order (Note that the purchase order is created on purchasing module).
STEP 7: Step 7 is an online approval process. In this step, match the amount and quantity of the invoice to the purchase order, inspection information, and the information received. Make sure whether they met tolerances.
STEP 8: Two states occur,
- Tolerance meet
- Tolerance not meet
If tolerance meets, place no holds on the invoice. Finally, the invoice approves for payment.
If tolerance does not meet, place a hold on the invoice, and proceed for step 8.
STEP 9: Either the reason behind the hold should be fixed or proceed for manual release of the hold.
STEP 10: Repeat the invoice approval process once you resolve the hold. If tolerances met, the invoice is authorized for payment.
Difference between 2-way vs 3-way matching?
From the above 2-way and 3-way matching explanation, you might get a clear picture regarding the topic. Here is the difference between the 2-way and 3-way matching in simple terms.
With the help of 2-way matching, you can make sure that all your data on the purchase order and your invoice aligns. And with the help of 3-way matching, you go with the one step further and can make your certain data on the purchase order, invoice, and the sales receipt the same.
Which is the better matching? 2-way or 3-way matching?
Whether 2-way matching or 3-way matching, both include benefits as well as drawbacks.
It’s more efficient to check the documents in pairs, which is easier if you use 2-way matching. But, with the help of 3-way matching, you can determine more mistakes than 2-way matching. The reason behind this is you are checking 3 documents instead of two documents.